 Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8-UBA_Ysgdsvideo
Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8-UBA_YsgdsvideoConcepts covered:neuron potentials, sodium-potassium pump, voltage-gated channels, myelin sheaths, action potential propagation
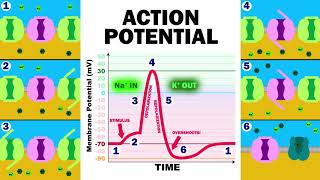
The video explains the mechanisms of neuron potentials, focusing on resting, graded, and action potentials. It details how ions and channels contribute to these processes, emphasizing the role of the sodium-potassium pump, voltage-gated channels, and myelin sheaths in action potential propagation.
chapter
1
THE ACTION POTENTIAL
Concepts covered:neuron potentials, sodium-potassium pump, voltage-gated channels, myelin sheaths, action potential propagation
The video explains the mechanisms of neuron potentials, focusing on resting, graded, and action potentials. It details how ions and channels contribute to these processes, emphasizing the role of the sodium-potassium pump, voltage-gated channels, and myelin sheaths in action potential propagation.
Question 1
Myelin sheaths increase neuron transmission speed.
Question 2
What triggers neurotransmitter release at axon terminals?
Question 3
The sodium-potassium pump transfers three sodium ions out and _____ potassium ions in.
Question 4
CASE STUDY: A neuron is exposed to a toxin that blocks voltage-gated sodium channels.
What happens to action potential generation?
Question 5
Action potentials can travel backwards along the axon.
Question 6
What maintains a neuron's resting potential?
Question 7
Action potentials occur at nodes of Ranvier due to _____ conduction.
Question 8
CASE STUDY: A patient has a genetic mutation affecting myelin sheath formation.
What is the impact on nerve signal speed?
Question 9
Voltage-gated channels open at specific voltages.
Question 10
How does myelin affect action potential speed?
Question 11
During the absolute refractory period, sodium channels are briefly _____.
Would you like to create and run this quiz?
yesCreated with Kwizie
