 Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dF5lB7gRtcAvideo
Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dF5lB7gRtcAvideoConcepts covered:redox reactions, oxidation states, oxidizing agents, reducing agents, electron transfer
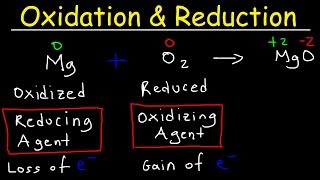
The video provides an introduction to oxidation and reduction reactions, explaining the concept of redox reactions where electrons are transferred between elements. It covers the identification of oxidizing and reducing agents, the role of oxidation states, and how to determine if a reaction is a redox reaction, using examples such as magnesium oxide formation and zinc reacting with hydrochloric acid.
Table of Contents1.Identifying Oxidation and Reduction in Chemical Reactions2.Identifying Redox Reactions in Chemical Processes3.Identifying Redox Reactions in Chemical Processes
chapter
1
Identifying Oxidation and Reduction in Chemical Reactions
Concepts covered:oxidation states, methane, zinc, oxidizing agent, reducing agent
The chapter explains the process of identifying oxidation states in chemical reactions, using examples of methane reacting with oxygen and zinc reacting with hydrochloric acid. It details how to determine which substances are oxidized or reduced, and how to identify the oxidizing and reducing agents in these reactions.
Question 1
Methane is oxidized in the reaction with oxygen gas.
Question 2
Identify the reducing agent in zinc reaction.
Question 3
Oxygen gas is the _____ agent in methane combustion.
Question 4
CASE STUDY: In a laboratory, a student observes zinc reacting with hydrochloric acid. They must identify the changes in oxidation states and the agents involved.
Identify the incorrect statement about zinc and HCl reaction.
Question 5
CASE STUDY: During a chemistry exam, a student must analyze a reaction where methane reacts with oxygen. They need to identify the substances oxidized and reduced.
Select three correct statements about methane and oxygen reaction.
Question 6
Hydrochloric acid is reduced in the reaction with zinc.
Question 7
What is oxidized in methane combustion?
Question 8
Hydrogen in HCl changes oxidation state from +1 to _____.
Question 9
CASE STUDY: A chemical engineer is analyzing a reaction where methane combusts in a controlled environment. They need to determine the substances involved in oxidation and reduction processes.
Identify the incorrect statement about methane combustion.
Question 10
Zinc is oxidized when reacting with hydrochloric acid.
Question 11
What happens to oxygen in methane reaction?
Question 12
In peroxide, oxygen's oxidation state is _____.
Question 13
Oxygen gas acts as the oxidizing agent in the reaction.
Question 14
Determine the oxidizing agent in zinc reaction.
Question 15
In methane, carbon's oxidation state changes from -4 to _____.
Question 16
Metals typically act as reducing agents in reactions.
Question 17
What is the oxidation state of carbon in CO2?
Question 18
In zinc and HCl reaction, zinc is the _____ agent.
chapter
2
Identifying Redox Reactions in Chemical Processes
Concepts covered:redox reaction, oxidation state, synthesis reaction, decomposition reaction, electron transfer
The chapter explains how to identify redox reactions within synthesis and decomposition reactions by analyzing changes in oxidation states. It highlights that a redox reaction involves a transfer of electrons, often indicated by the presence of a pure element on one side of the reaction and its compound form on the other.
Question 19
All single replacement reactions are redox reactions.
Question 20
What indicates a redox reaction in a synthesis?
Question 21
If oxidation state doesn't change, it's not a _____ reaction.
Question 22
CASE STUDY: A chemical engineer is analyzing a reaction involving magnesium and oxygen. The reaction forms magnesium oxide, and the engineer needs to determine if it's a redox reaction.
Identify the incorrect redox reaction indicator.
Question 23
Presence of pure element suggests a redox reaction.
Question 24
Determine the redox reaction in decomposition examples.
Question 25
A pure element on one side indicates a _____ reaction.
Question 26
CASE STUDY: A student is tasked with identifying redox reactions in a series of chemical equations. One equation involves zinc reacting with hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
Identify the incorrect redox reaction indicator.
Question 27
Combination reactions are never redox reactions.
Question 28
What is a quick way to identify redox?
Question 29
A synthesis reaction can sometimes be a _____ reaction.
Question 30
Oxidation state change indicates a redox reaction.
Question 31
Which reaction type is always a redox?
Question 32
In a redox reaction, there's a transfer of _____ .
Question 33
A reaction with no pure elements is always redox.
Question 34
Identify a redox reaction from these examples.
chapter
3
Identifying Redox Reactions in Chemical Processes
Concepts covered:redox reactions, combustion, single replacement, double replacement, pure elements
The chapter explains how to identify redox reactions by examining the presence of pure elements on one side of the reaction and their incorporation into compounds on the other side. It highlights that combustion and single replacement reactions are always redox, while double replacement reactions, including acid-base and precipitation reactions, are not.
Question 35
Combustion reactions are always redox reactions.
Question 36
Apply the rule to identify a redox reaction.
Question 37
All combustion reactions are _____ reactions.
Question 38
CASE STUDY: A chemical engineer is analyzing a reaction involving methane combustion.
Identify the incorrect statement about redox reactions.
Question 39
CASE STUDY: A teacher is preparing a quiz on chemical reactions.
Select three characteristics of redox reactions.
Question 40
Double replacement reactions can be redox reactions.
Question 41
Identify a redox reaction from given examples.
Question 42
Double replacement reactions, including precipitation, are never _____ reactions.
Question 43
CASE STUDY: A student is classifying reactions in a lab experiment.
Identify the incorrect classification of reactions.
Question 44
Single replacement reactions are always redox reactions.
Question 45
Analyze why a reaction is not redox.
Question 46
A reaction with a pure element on one side is a _____ reaction.
Would you like to create and run this quiz?
yesCreated with Kwizie
