 Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ueqh5YqpIHovideo
Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ueqh5YqpIHovideoConcepts covered:ingestion, digestion, absorption, enzymes, villi
The video provides an in-depth explanation of the human digestive system, covering key processes such as ingestion, digestion, absorption, and transport of nutrients. It details the roles of various digestive organs, enzymes, and the importance of structures like villi and microvilli in nutrient absorption, as well as the regulation of digestive juices and the impact of fiber on digestion.
Table of Contents1.The Process of Digestion in Human Physiology2.Structure and Function of the Small Intestine3.Digestion of Starch: From Amylase to Glucose Absorption4.Detailed Structure and Function of Intestinal Villi5.The Role of Fiber in Digestion
chapter
1
The Process of Digestion in Human Physiology
Concepts covered:digestion, macromolecules, enzymes, absorption, catabolic reactions
Chapter 6.1 focuses on the process of digestion, detailing the breakdown of macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates into their smaller components. It also explains the roles of ingestion, absorption, and transport, highlighting the importance of enzymes in facilitating these catabolic reactions without increasing body temperature.
Question 1
Digestion involves only the physical breakdown of food.
Question 2
What is the process of taking in food?
Question 3
How do enzymes facilitate digestion?
Question 4
CASE STUDY: A patient is diagnosed with a deficiency in pancreatic enzymes. This condition affects the digestion of macromolecules in the small intestine.
All of the following are affected except...
Question 5
CASE STUDY: A biochemist is developing a new supplement to aid in the digestive process by enhancing enzyme activity.
Select three correct outcomes of enhanced enzyme activity...
chapter
2
Structure and Function of the Small Intestine
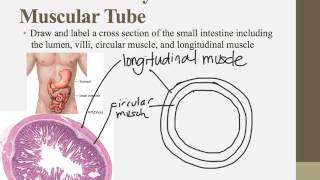
Concepts covered:small intestine, villi, longitudinal muscle, circular muscle, peristalsis
The chapter explains the structure and function of the small intestine, focusing on its muscular layers and the role of villi in digestion. It also describes the process of peristalsis, which moves food through the digestive tract using muscular contractions, independent of gravity.
Question 6
Peristalsis allows digestion without relying on gravity.
Question 7
What is the function of the villi?
Question 8
How does peristalsis move food through the tract?
Question 9
CASE STUDY: During a surgery, a section of the small intestine is removed, and the surgeon needs to identify the layers of the intestine.
All of the following are correct layers except...
Question 10
CASE STUDY: A researcher is studying the efficiency of nutrient absorption in the small intestine.
Select three correct statements about the small intestine.
chapter
3
Digestion of Starch: From Amylase to Glucose Absorption
Concepts covered:starch, amylase, maltose, glucose, villi
The chapter explains the digestion process of starch, starting with its breakdown by amylase from the salivary glands and pancreas into maltose, and then further into glucose by another enzyme. The glucose is then absorbed by the small intestine, specifically through the villi.
Question 11
Maltose is further broken down into glucose in the small intestine.
Question 12
How does glucose get absorbed in the small intestine?
Question 13
Where is amylase produced?
Question 14
CASE STUDY: A patient has a genetic mutation that prevents the production of salivary amylase. They consume a meal rich in starch. What impact will this have on their digestion?
All of the following are correct applications of starch digestion except:
Question 15
CASE STUDY: A person consumes a meal devoid of any starch but rich in proteins and fats. How will this affect the activity of amylase in their digestive system?
Select three correct outcomes of this scenario:
chapter
4
Detailed Structure and Function of Intestinal Villi
Concepts covered:intestinal villi, microvilli, epithelial cells, lacteal, capillaries
The chapter provides a detailed examination of the structure and function of intestinal villi. It explains how villi and microvilli increase the surface area for absorption and describes the roles of epithelial cells, lacteals, and capillaries in nutrient absorption and transport.
Question 16
Villi increase surface area for absorption in the small intestine.
Question 17
What is the primary function of villi?
Question 18
What does the lacteal absorb and transport?
Question 19
CASE STUDY: Researchers are developing a drug that targets the epithelial cells of the small intestine to enhance nutrient absorption.
All of the following are correct about epithelial cells except:
Question 20
CASE STUDY: A new study shows that certain diseases can damage the lacteals within the villi, impairing fat absorption.
Select three correct outcomes of lacteal damage:
chapter
5
The Role of Fiber in Digestion
Concepts covered:fiber, cellulose, digestion, feces, bile
Fiber, primarily found in plant cell walls, is crucial for efficient digestion as it adds bulk to food, aiding its movement through the digestive system and preventing decay in the intestines. It also helps you feel full without adding calories, and the undigested remnants, including cellulose and bile, form the bulk of feces.
Question 21
Fiber is digested and absorbed in the small intestine.
Question 22
How does fiber help in feeling full?
Question 23
Why might you see corn in feces?
Question 24
CASE STUDY: A patient complains of chronic constipation and a feeling of fullness. They have a diet consisting mainly of processed foods and very little fruits or vegetables.
All of the following are correct recommendations except:
Question 25
CASE STUDY: A researcher is studying the components of feces in individuals with different diets. They need to identify what remains undigested in the feces.
Select three correct undigested components out of the following:
Would you like to create and run this quiz?
yesCreated with Kwizie
