 Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0fOTBs8_dHwvideo
Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0fOTBs8_dHwvideoConcepts covered:spinal cord anatomy, gray matter, white matter, tracts, nuclei
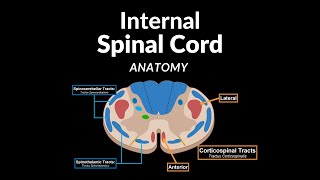
The video discusses the internal anatomy of the spinal cord, focusing on the distribution of gray and white matter, as well as the tracts and nuclei within. It covers the structure of gray matter, including the anterior, posterior, and lateral horns, and details the white matter divisions into posterior, lateral, and anterior funiculi.
Table of Contents1.Anatomy of the Central Nervous System: Internal Surface of the Spinal Cord2.Microscopic Anatomy of the Spinal Cord3.Gray Matter Structure and Nuclei in the Spinal Cord4.Organization of White Matter in the Spinal Cord5.Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
chapter
1
Anatomy of the Central Nervous System: Internal Surface of the Spinal Cord
Concepts covered:Central Nervous System, Spinal Cord Anatomy, White Matter, Gray Matter, Tracts and Nuclei
Exploration of the internal surface of the spinal cord, focusing on the distribution of white and gray matter, anatomy of tracts, and nuclei within the spinal cord.
Question 1
How do gray and white matter differ in the spinal cord?
Question 2
Where is gray matter located in the spinal cord?
Question 3
What should you study first for spinal cord anatomy?
chapter
2
Microscopic Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
Concepts covered:Spinal Cord, Gray Matter, White Matter, Neurons, Myelinated Axons
The internal surface of the spinal cord comprises gray matter rich in nerve cell bodies and dendrites, and white matter rich in myelinated axons and glia cells. The distinction between gray and white matter is due to the colorless nature of neurons, with gray matter appearing gray under a microscope.
Question 4
How do gray and white matter differ structurally?
Question 5
What are structures in white matter called?
Question 6
What does gray matter primarily consist of?
chapter
3
Gray Matter Structure and Nuclei in the Spinal Cord
Concepts covered:Gray matter, Spinal cord, Anterior horn, Posterior horn, Lateral horn
The gray matter in the spinal cord consists of three main horns: anterior, posterior, and lateral, each associated with distinct functions and nuclei. The anterior horn primarily contains motor nuclei, the posterior horn receives sensory information, and the lateral horn houses sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers.
Question 7
What type of nuclei does the anterior horn contain?
Question 8
Where is the lateral horn located?
Question 9
Which nucleus modulates sensory inputs like pain?
chapter
4
Organization of White Matter in the Spinal Cord
Concepts covered:white matter, spinal cord tracts, ascending tracts, descending tracts, voluntary movements
The white matter of the spinal cord consists of tracts or bundles of fibers divided into posterior, lateral, and anterior funiculi, facilitating the transmission of sensory and motor information. Ascending tracts relay conscious sensory information to the cerebrum, while descending tracts control voluntary and involuntary movements.
Question 10
What are the three portions of white matter?
Question 11
Which tract relays unconscious proprioceptive sensation?
Question 12
Which tract is responsible for conscious proprioception?
chapter
5
Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
Concepts covered:Spinal Cord, Sensory Tracts, Motor Tracts, Posterior Funiculus, Corticospinal Tract
The chapter discusses the sensory and motor tracts of the spinal cord, detailing the functions and pathways of various tracts such as the posterior funiculus, spinothalamic tract, corticospinal tract, rubrospinal tract, and more. It explains how these tracts are responsible for conscious and unconscious sensations, movements, and coordination.
Question 13
Where is the medial longitudinal fascicle located?
Question 14
Where is the fasciculus cuneatus found?
Question 15
What does the fasciculus gracilis conduct?
Would you like to create and run this quiz?
yesCreated with Kwizie
