 Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zJNx1DDqIVovideo
Created from Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zJNx1DDqIVovideoConcepts covered:Electron Transport Chain, Aerobic Respiration, ATP generation, Mitochondrial membrane, ATP synthase
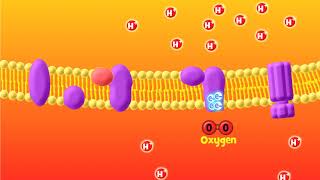
The electron transport chain is the crucial stage in aerobic respiration where most ATP is generated. It involves a series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transport electrons to create a high concentration of hydrogen ions, ultimately leading to ATP production through ATP synthase.
Table of Contents1.Electron Transport Chain: The Powerhouse of ATP Production2.Oxygen's Vital Role in ATP Production3.Hydrogen Ion Flow and ATP Synthase Mechanism
chapter
1
Electron Transport Chain: The Powerhouse of ATP Production
Concepts covered:Electron Transport Chain, ATP Production, Mitochondrion, Protein Complexes, Hydrogen Ion Pumping
The electron transport chain, located in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion, is where the majority of ATP is generated through the transfer of electrons and pumping of hydrogen ions. This process involves a series of protein complexes that create a high concentration of hydrogen ions in the intermembrane space, essential for ATP synthesis.
Question 1
What is the primary function of the electron transport chain?
Question 2
What role does electron movement play in cellular respiration?
Question 3
Why is a high proton concentration crucial in mitochondria?
chapter
2
Oxygen's Vital Role in ATP Production
Concepts covered:Oxygen, Electron Transport Chain, ATP Production, Hydrogen Ions, ATP Synthase
Oxygen plays a crucial role in the electron transport chain by accepting electrons and hydrogens to form water, essential for ATP production. The process involves ATP synthase utilizing a high concentration of hydrogen ions to generate ATP efficiently.
Question 4
What happens if the electron transport chain stops?
Question 5
How does ATP synthase facilitate ATP production?
Question 6
Why do cells need oxygen in cellular respiration?
chapter
3
Hydrogen Ion Flow and ATP Synthase Mechanism
Concepts covered:Hydrogen ions, ATP synthase, Electron transport chain, Respiration, ATP production
Hydrogen ions flow through ATP synthase from high to low concentration, causing ATP production through a turbine-like spinning mechanism. The electron transport chain in respiration generates 30 to 34 ATP molecules per glucose, with a microscopic hydroelectric dam analogy.
Question 7
What does ATP synthase require to produce ATP?
Question 8
What should you do after watching the respiration video?
Question 9
How many ATPs are produced per glucose in respiration?
Would you like to create and run this quiz?
yesCreated with Kwizie
